1-The primary consideration when enhancement is noted related to the optic nerve is differentiation between enhancement of the actual nerve and enhancement of the adjacent meningeal lining (optic nerves are lined by meninges rather than schwann cells seen with peripheral nerves.
2-When the nerve itself is clearly involved and when nerve enhancement is present, the next determination is whether or not there is mass-like enlargement to suggest optic glioma.
3- If it demonstrates only minimal diffuse enlargement and associated edema (T2 hyper intensity). The primary differential considerations are optic neuritis or optic nerve vasculitis (most commonly related to infection, radiation, or autoimmune disorders). Optic neuritis is much more common and is the correct diagnosis in this case.
 |
| Optic nerve neuritis. |
1-Optic neuritis is defined as inflammation of the optic nerve.
2-It is one of the causes of acute loss of vision associated with pain.
3-Optic neuritis can be the initial episode for a patient who will subsequently develop multiple sclerosis.
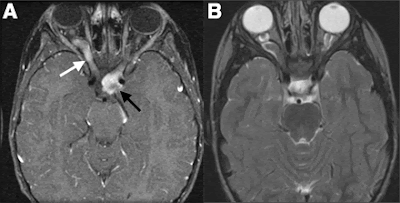
4-Thin fat-suppressed T2-weighted images, such as short tau inversion recovery sequences, through the optic nerves may show characteristic high-signal intensity foci in the minimally or nonexpanded nerve.
5-These lesions frequently enhance following intravenous contrast administration, which is not seen in a healthy optic nerve. In our case DWI was also used which shows expanded left optic nerve with bright signal on DWI and enhancement on CEMRI. In this patient MRI brain had no evidence of MS.

No comments:
Post a Comment